
India’s steel industry stands at the forefront of the country’s industrial and economic growth. As the second-largest steel producer globally, it plays a critical role in shaping India’s infrastructure and other key sectors. However, the industry faces challenges, including high production costs, environmental concerns, and infrastructure bottlenecks. At the same time, it is exploring new opportunities, especially through technological advancements and digital transformation, paving the way for a more sustainable and competitive future.
Growth Prospects for the Indian Steel Industry
India’s steel production has been on a steady rise over the past decade, fuelled by robust domestic demand across sectors like construction, automotive, and capital goods. According to the government’s National Steel Policy (NSP), India aims to increase its crude steel production capacity to 300 million tonnes by 2030, up from the current levels. In the fiscal year 2018-2019, India’s steel production reached 110.9 million tonnes, and the industry has been growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%.
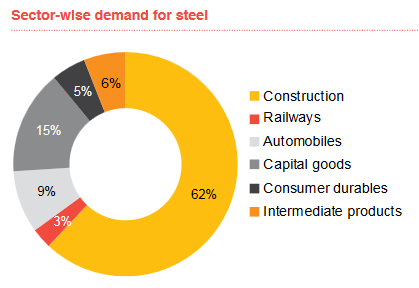
The construction sector accounts for 62% of steel demand in India, and the government’s investment in infrastructure projects, such as Bharatmala for road development and Sagarmala for port connectivity, will likely continue to drive demand. Urbanization is another key driver. The government’s focus on building smart cities and affordable housing also supports the growing need for steel, bolstering the industry’s long-term growth prospects.
Key Challenges in the Indian Steel Industry

Despite the promising outlook, India’s steel sector is grappling with several challenges:
High Production and Capital Costs: Steel production involves high costs, especially with India’s reliance on imported coking coal. This adds cost volatility, impacting maintenance budgets and planning.
Logistical Bottlenecks: Due to outdated infrastructure, transporting raw materials and finished products becomes costly and inefficient, complicating timely maintenance schedules and resource allocation.
Environmental and Energy Pressures: As a major energy consumer, the steel industry faces strict emissions regulations, requiring maintenance strategies that also prioritize sustainability.
- Digital Adoption Needs: While technologies like IoT and AI offer predictive maintenance to prevent breakdowns and downtime, their implementation requires upfront investment and a skilled workforce, both current challenges for the sector.
- Skill Gaps for Advanced Maintenance: As digital tools become essential, there’s a growing need for upskilling workers to maintain and operate these technologies effectively.
Digital Transformation and Technology Adoption
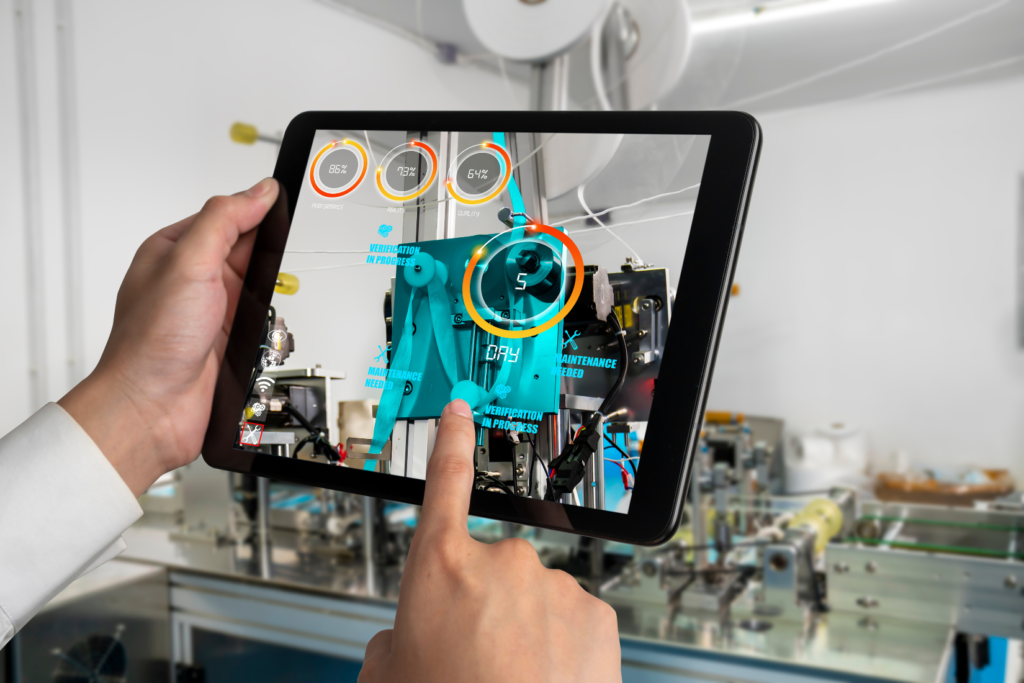
Digital disruption presents a critical opportunity for the Indian steel industry to overcome these challenges. As the sector seeks to modernize and become more competitive, digital technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and automation are transforming steel production processes.
IoT technologies enable real-time monitoring of equipment, optimizing operations and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance. IoT sensors are embedded in manufacturing machinery to detect wear and tear, preventing breakdowns and improving operational efficiency.
AI-powered predictive analytics further enhances the steel production process. By analysing large volumes of historical and real-time data, AI helps manufacturers optimize processes, predict equipment failures, and fine-tune production to meet demand fluctuations.
Sustainability and the Green Steel Initiative

The push for sustainability has become a top priority for the Indian steel industry. Green steel initiatives, which focus on reducing carbon emissions in steel production, are gaining attention. As countries around the world implement stringent environmental regulations, India’s steel producers must adopt cleaner production methods to remain competitive, particularly in the export market.
Technologies like hydrogen-based Direct Reduced Iron (DRI) and Carbon capture and storage (CCS) are being explored to reduce the carbon footprint of steel production. While these technologies are still in the early stages of adoption in India, they represent a significant step toward producing sustainable steel.
India’s steel industry is also focusing on improving energy efficiency. Advanced technologies, such as AI-powered energy management systems, help optimize energy consumption by identifying inefficiencies in real time and suggesting corrective measures. These systems can significantly reduce a plant’s overall energy usage, lowering both costs and emissions.
The Future of India’s Steel Industry: Opportunities and Strategic Initiatives
As the Indian steel industry looks toward the future, digital transformation will play a pivotal role in driving both growth and sustainability. The path to modernization and increased competitiveness will require embracing disruptive technologies, investing in green steel production, and optimizing processes to meet the demands of a growing domestic and global market.
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative, led by the Ministry of Heavy Industry, is a key government program aimed at creating experiential centres and fostering innovation in the steel sector. The program emphasizes smart manufacturing and the integration of digital technologies across the steel value chain.
Collaborative efforts between the government, industry players, and technology providers are crucial for realizing the sector’s full potential. Public-private partnerships can facilitate investments in digital infrastructure, advanced manufacturing, and research and development, all of which are essential for the steel industry’s continued growth.
Workforce upskilling is another critical area of focus. As the industry embraces new technologies, there is a growing need for a digitally skilled workforce that can operate and maintain advanced equipment. Training programs and partnerships with academic institutions can help bridge this skills gap and ensure that workers are prepared for the digital transformation.

Conclusion
The steel industry is at a critical juncture, where sustainability and technological innovation are essential for long-term success. The move toward net-zero emissions is both a response to climate imperatives and a strategic effort to remain competitive in an eco-conscious market. Solutions like CIMCON’s VIBit for predictive maintenance, combined with the CIMCON’s iEdge 360 Platform and CIMcloud, offer a comprehensive digital approach to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive sustainable production.
The CIMCON 360 Platform enables real-time data integration across the steel production process, fostering data-driven decision-making and ensuring optimized maintenance schedules. With CIMcloud, steel manufacturers gain centralized access to asset performance insights, predictive analytics, and secure cloud storage, supporting a proactive maintenance strategy that minimizes downtime and improves equipment lifespan.
India’s steel sector, in particular, must balance rising demand with a commitment to reducing environmental impact. By embracing digital transformation and prioritizing sustainable practices through CIMCON’s platforms, the industry is well-positioned to achieve its growth ambitions and maintain its role in driving India’s economic development and global leadership in steel production.
Schedule a live demo to discover how CIMCON’s innovative platforms can support your digital transformation journey.

