What is Edge Computing?
We are in the midst of significant transformation regarding the way we handle and manage data,, thanks to the digitization of industries. The transition is so compelling that it is called Industry 4.0. From the First Industrial Revolution which was spurred by the use of steam powered engines, to the second industrial revolution when steam was replaced by water and electricity enabling mass production, the fourth industrial revolution or Industry 4.0 will take what was started in the third which was characterized by personal computer and the internet besides information and communication technology (ICT) and enhance it with smart and autonomous systems fueled by data and machine learning With the advent of Industry 4.0, we all have heard about the word “Edge” and how it is impacting this era of IoT Technology. Organizations around the world use cloud computing as a centralized server. Generally, it is a distant server, which increases the frequency of communications; this becomes a limitation for applications that requires real-time responses.
This limitation has given rise to edge computing in which nodes can be centralized, distributed, or at the end of the network (the edge), allowing for a more distributed processing of the information generated by peripheral devices. This technology allows computation at the network edge so that computing happens near data sources. In edge computing, the end device not only consumes data but also produces data. It works on downstream data on behalf of cloud services and upstream data on behalf of IoT services.
How to Use Edge Computing for Smart Sensors
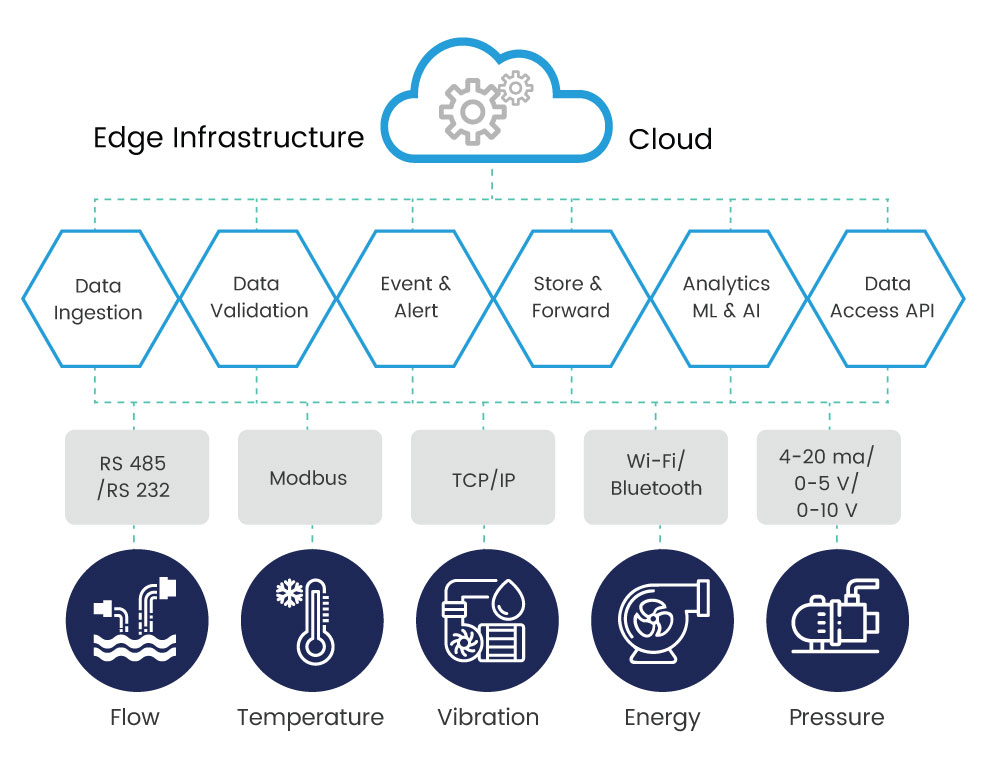
The image above demonstrates how to use edge technology; the devices and sensors interact directly with the end-user. Although some devices can send real-time data, not all devices have that capacity. In that case, they send information to the Edge infrastructure. Edge infrastructure is the distributed data centers that provide real-time data analysis, visualization filtering, and optimization. Since they are located closer to the end-user, they perform a lot of calculations for a large volume of data. With this capability, the edge reduces data flow and the costs of using cloud services as well as reducing end-user response time and latency.
Edge Computing Applications for Smart Sensor
Edge computing devices can be used for a variety of applications, including the following:
Health: Edge technology can be used to monitor devices in the health industry and predict the machine health in order to improve the efficiency
Remote Monitoring: Collecting and analyzing data from sensors and other field devices, remote monitoring provides industries with insight and visibility into the performance of their machines, processes, and people. Even sensor data can be accessed in real time from any location.
Predictive Maintenance: Edge computing, coupled with AI/ML algorithms, enables users to more accurately anticipate when machine maintenance will be required based on real-time data from the machine itself.
Benefits of using Edge Computing
Improved Speed/Latency: The reason why Edge computing is used in industrial automation industries is because of the speed to send data. This is called latency. In the world of automation, real time data decision making capabilities are important for functioning of devices and saves the client a ton of money in unplanned downtime
Improved Security: Edge computing provides greater security than the cloud. Although edge devices can also get hacked as they do not hold a great amount of data or complete sets of data, so the hackers do not find the data useful.
Reduce Operational Cost: Data storage costs can be costly. Users also need to implement higher bandwidth to handle huge loads of data, leading to costlier data storage units. Edge computing can keep the costs lower by reducing the amount of data being moved back and forth to the cloud.
Scalability: Endpoint hardware and edge devices often cost less than adding more computational resources within a centralized data center, thereby making it more efficient for organizations to scale at the edge.
Real Examples of Edge Device Application for Smart Sensors
Intelligent edge terminal units like CIMCON iEdge 360 provide multiple networks, including industry-standard communication networks; that way, you can connect your existing and new sensors to a single device. The edge device transforms data on as per use case basis. It sends raw and transformed data to the public or on premise IoT platform for various visualization and analytics requirements.
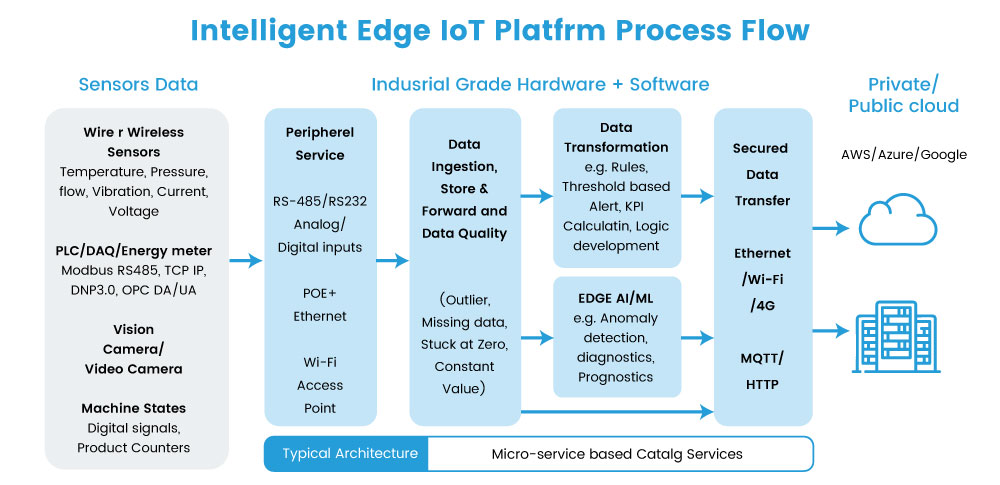
CIMCON iEdge 360 packs 30+ years of experience connecting industrial assets such as machines, sensors, camera, vibration sensors, SCADA systems and PLC’s using a variety of protocols and interfaces over wired or wireless networks to deliver the outcomes that our customers demand and expect from us Click the link or e-mail us to schedule a demo of the platform



Leave a Reply