In 4 years, more than 30% of businesses and organizations will include edge computing in their cloud deployments to address bandwidth bottlenecks, reduce latency, and process data for decision support in real time. Edge computing accomplishes this by bringing the businesses’ computational processes closer to the data sources, increasing the speed of these actions. Additionally, even if a single node is unreachable, the service should still be accessible to users. In this way, edge computing promises to deliver Internet of Things (IoT) reliably and speed while taking more care of security, data privacy.
What’s more, 69% of organizations say that prioritizing edge-based analytics will improve their ability to meet IoT objectives for specific use cases.
Industries including Manufacturing, Water & Wastewater, Utilities and Building, are implementing hybrid strategies to enable real-time analytics such as Machine Anomaly detection and diagnostics, Quality Analytics, Energy Analytics, and OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). First, anomaly detection on the edge leverages Machine Learning to monitor machine health, detect anomalous data from sensors, and reduce the time it takes to get critical information. Advanced notice of anomalous machine behavior gives maintenance employees to prevent breakdowns before they occur, saving the business time, money, and resources.
Additionally, running quality analytics on the edge enable faster decision making , which is important for many industries. This type of data analysis on the edge is important for businesses which use real-time data to improve productivity, require solutions that scale over time, or reside in a fast-paced environment full of unexpected changes. Edge computing gives you access to analytics and actionable insight on edge, right where the data is generated.
Also, energy analytics on the edge has allowed utility companies to get real-time data at remote energy production facilities such as wind turbine farms or solar farms. It is not practical for remote equipment at these locations to quickly transmit data to and from the cloud, slowing the data analytics process. However, if data is quickly processed on edge computing devices, employees have access to real-time data which reflects the current state of energy production.
Lastly, Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures how well a manufacturing operation is utilized compared to its full potential, measuring the percentage of manufacturing time that is truly productive. This includes measuring the speed at which the parts are produced (the performance), the quality of the parts which are being manufactured (the quality), and the number of interruptions to the manufacturing process (the availability). A perfect score of 100% indicates that all the manufactured parts are good, they were produced at maximum speed, and they were produced without interruption. Measuring these aspects is a best practice for any manufacturing operation. Bringing OEE onto the edge allows businesses to measure their Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) easily and pivot their business with agility.
Edge-enabled machines provide the data to give you insight and foresight into manufacturing or the utility floor near your asset; you can take preventative corrective action, even when the opportunity to prevent problems is very small.
CENTRALIZED CLOUD ANALYTICS STUMBLE IN CRITICAL MANUFACTURING AREAS
Many enterprises have adopted cloud first strategies. They have married their workflows to cloud platforms to connect low cost, elastic global infrastructure with rich device data. Initially, this approach allowed these organizations to accelerate deployment of connected products and industrial internet efforts. However, as they scale their digital transformation efforts, cloud-only approaches limit growth because of delays to transmit data from devices to the cloud and to transmit analytics from the cloud back to devices. IoT use cases on the manufacturing floor often have unique, real-time data analysis needs. It is not always practical, economical, or even lawful to move, store, and analyze IoT data on a core cloud infrastructure. Many manufacturing professionals recognize these limitations. They cite security concerns, the high costs of repeatedly accessing data, reduced data accessibility, and the subsequently reduced ability to make real-time decisions as the top downfalls of analyzing IoT data in the cloud. The solution to these latency issues is to continue to scale businesses using edge computing.
Edge computing solutions, which converge hardware and software into increasingly smaller devices which run smarter analytics onboard, enable real-time decisions and insights. Momentum for edge IoT solution deployment is increasing at a faster rate in the manufacturing, utility, and building use cases.
Edge computing often incorporates Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. These techniques make the calculations performed on the edge even more efficient. That way, the system does not require the help of human operators to identify data irregularities which may point to a potential problem developing with a machine or system. The AI can flag anomalies in an actionable way so that machine breakdown can be prevented. Another use case for AI on the edge is the detection of defective parts in a manufacturing operation. This technology can be used to guide part inspectors or to identify patterns which may lead to the production of defective parts.
However, the accuracy of the models which AI uses for these purposes may degrade over time—this is where Machine Learning (ML) becomes important. ML is incorporated into the process to create a closed loop in which the computer contains supervisory programming which observes the accuracy of the AI model over time by analyzing data drifts within the AI model.
All these technologies are available through CIMCON’s versatile iEdge 360 Edge Computing Platform. This system is designed to integrate both wireless and wired sensors into the IoT network. The iEdge 360 platform compiles, validates, quality-checks, and processes the data. It efficiently uses bandwidth to store and forward data, creating a sensor data lake. The data collected is also used to nimbly detect anomalies in machine operation on the edge.
CIMCON iEdge 360 Edge Computing Platform enables multiple use cases:
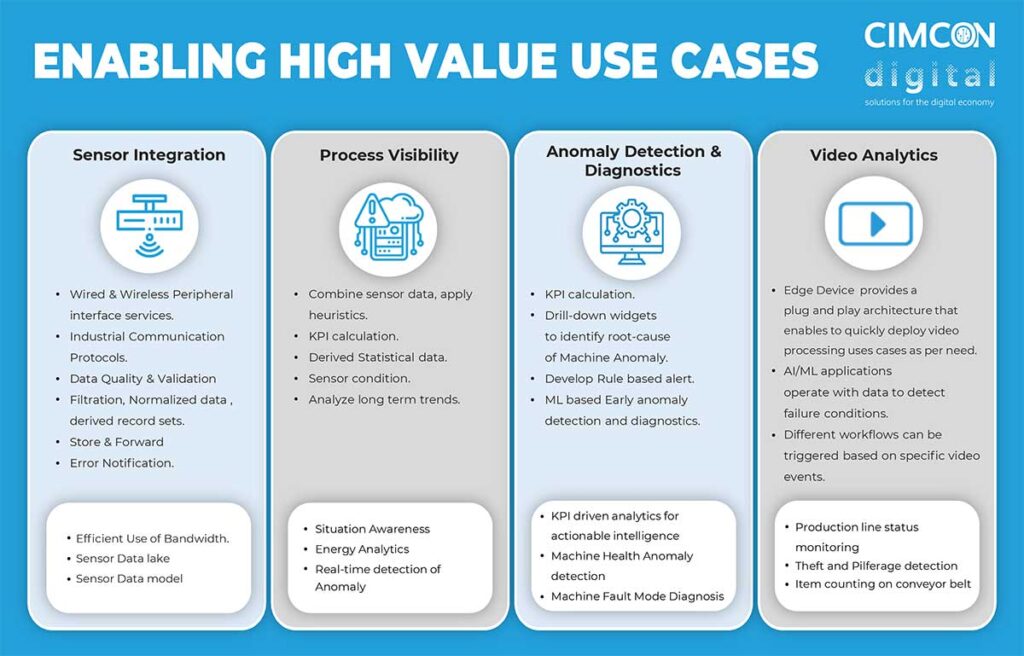
The platform gives users insights into machine operation and process data which would otherwise be unavailable. This includes automated KPI calculation, derived statistical data, and long-term trend analysis. This gives operators the process visibility they need for situational awareness, energy analytics, and real-time detection of anomalies. This helps you stay on top of your operational goals, efficiency objectives, and machine health status in a simple package which keeps your business running smoothly,
When an anomaly is detected, the iEdge 360 platform provides machine operators with the tools to determine the cause. Drill-down widgets and rule-based alerts couple with Machine Learning technology to enable easy machine diagnostics. Key Performance Indicator (KPI) calculations and machine fault mode diagnosis take the raw data collected by the system and turn it into actionable intelligence. Rather than allowing you to get lost in the sea of big data, the iEdge 360 platform pinpoints the important nuggets of information and presents it to you in an easy-to-understand manner. This allows operators to quickly fix the issue and get critical processes running again. Overall, these features reduce operational downtime, repair costs, and labor costs while increasing energy efficiency and production output.
In addition to the other actionable, useful features, CIMCON’s iEdge 360 Edge Computing Platform contains built-in video analytics capabilities. A plug and play architecture is included out of the box which makes including video analytics into your system simple. AI and ML technologies built into the platform use video data to detect equipment failure conditions, triggering one of several custom workflows based on the events in the video. This feature allows you to monitor your business for production line efficiency, item counting on a conveyor belt, and even theft prevention.
The iEdge 360 IoT Platform is designed for collecting sensor data at scale and transforming that data into actionable intelligence using its powerful on-board processor as well as its high-level, general-purpose programming language; it uses Python and Flowchart programming, among other easy-to-use features. In this way, the platform is extremely user-friendly—it is not designed to be difficult to understand or obscure like some of its competitors. Rather, it is streamlined to make your business operate at peak efficiency. Its powerful quad core processor with modern microservice based architecture allows Edge AI/ML Algorithms to transform data into actionable insight at the edge.
Additionally, edge hardware moves the computing resources closer to the data source. Therefore, it compiles and filters data rapidly, alleviating bandwidth challenges. The platform pushes intelligence, data processing, analytics, and communication capabilities close to the locations of the sensors which gather the data.
Do you want to improve your bandwidth utilization while simultaneously generating insights into machine health, operational efficiency, and Key Performance Indicators? Are you ready to move into the world of the Internet of Things? We can walk your business through its digital transformation smoothly and efficiently. We will enable you to meet your KPIs while reducing operational downtime and utilizing the data you generate.
Would you like to know more about CIMCON iEdge 360 Platform solutions? Just send a message to our IoT application engineering team, and we will be happy to answer all your questions and provide product demonstrations.



Leave a Reply