The Project
Arvind mills is a global leader in apparel manufacturing as well as one of the largest textile manufacturer from India. It is headquartered in Naroda, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India with one of its facilities in Santej, Gujarat, India. The company manufacturers cotton shirts, knits, and denim. For the manufacturing of the shirts and denim, the company pays high utilities for water and electricity.
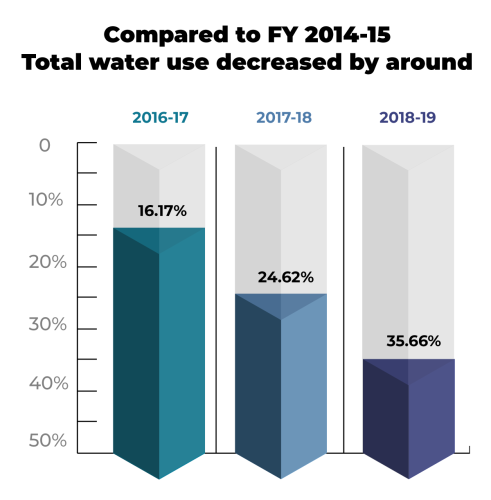
Arvind treats water as a natural resource, ensuring that their operations put as little stress on freshwater as possible. Every pair of blue jeans requires about 1880 gallons of water to manufacture. Additionally, 400 gallons of water are consumed in manufacturing one T-shirt. Arvind Mills wanted to optimize their water and electricity usage to decrease costs and increase machine efficiency. Arvind Mills installed flow meters and energy meters to measure the flow of water and the electricity consumed. However, they were unable to monitor these utilities in a centralized, thorough manner.
Introduction
The company, Arvind Mills, was founded in 1931 and headquartered in Gujarat, India. The company has more than 42,000 employees and generates annual revenue of $1 billion. The company manufactures apparel and textiles including its own brands like Flying Machine and Newport as well as licensed international brands like Tommy Hilfiger and Calvin Klein. Arvind also runs three clothing & accessories retail chains: the Arvind Store, Unlimited, and Megamart.
The Work
The work includes design, testing, supply, installation, and commissioning of a Centralized Energy Analytics System with a Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) / Edge Units and Analytics Application for the knit unit and shirting unit This equipment was used to monitor utilities in the Santej Mill production line to improve the machine health, optimize water usage, and fine-tune energy consumption. It was also be used to reduce unplanned manufacturing unit downtime.
Scope
The project scope included design, manufacturing, supplying, installing, commissioning, and documenting the SCADA system consisting of an RTU with 10 analog inputs and an energy meter connected over a wired network with a SCADA Software.